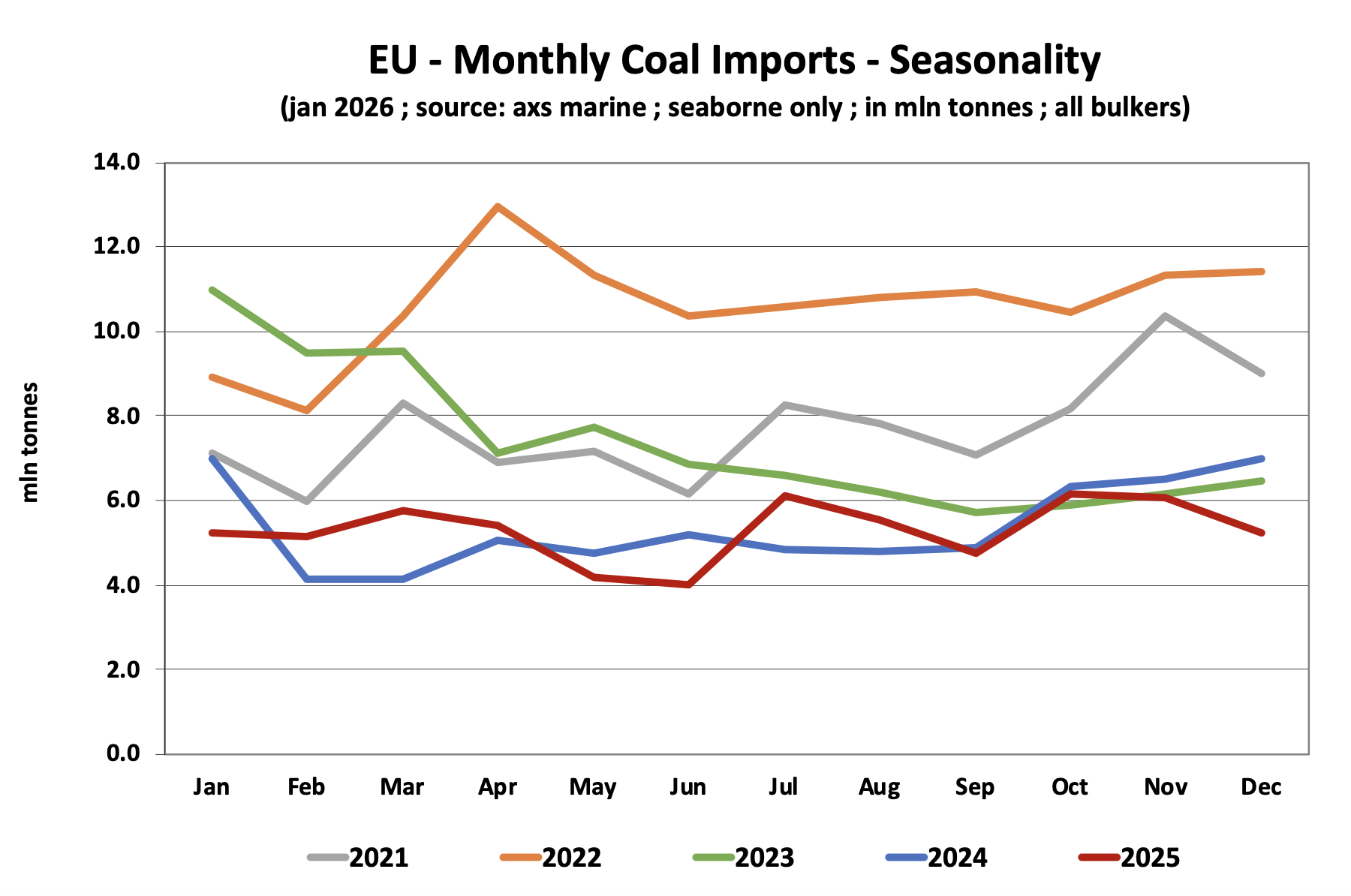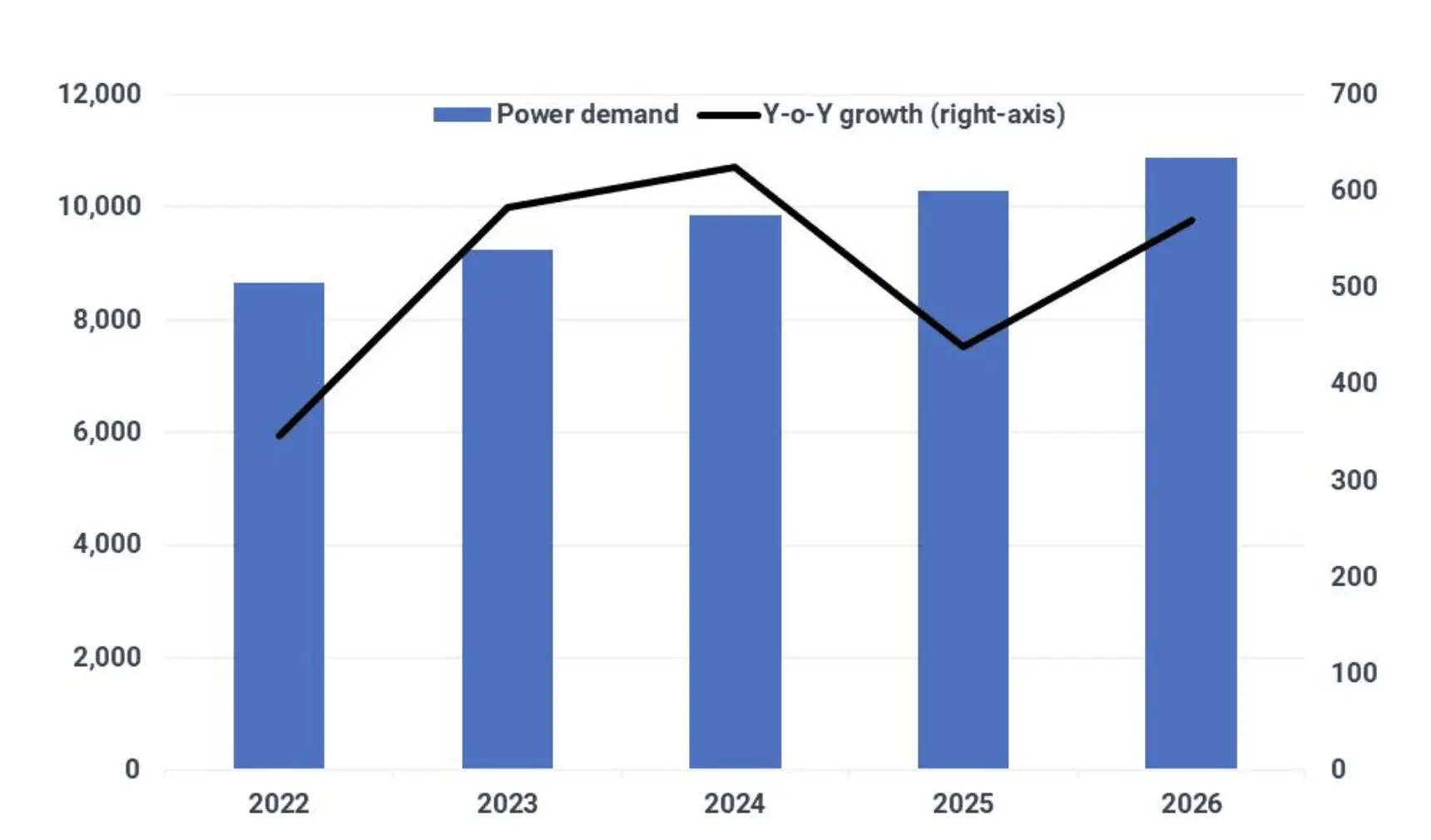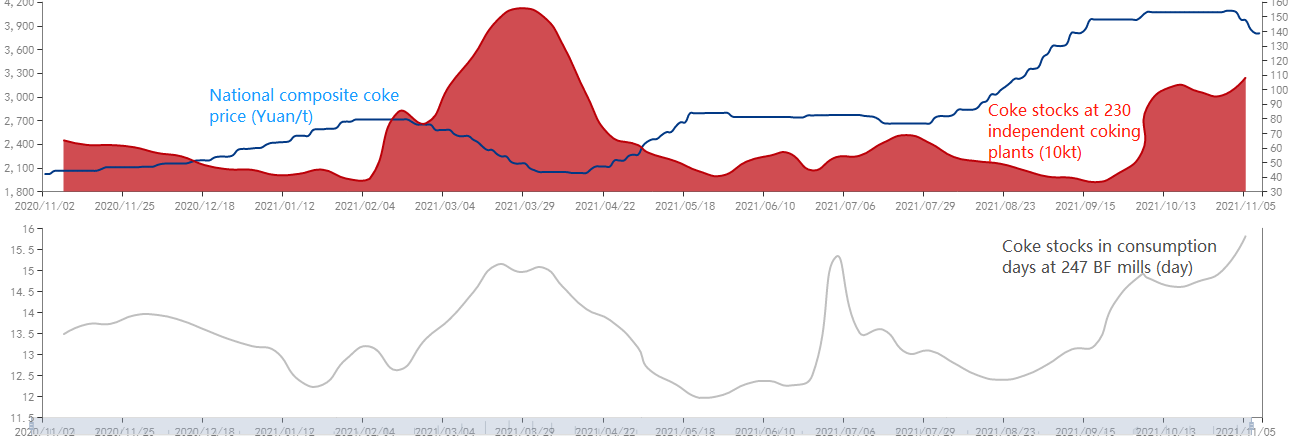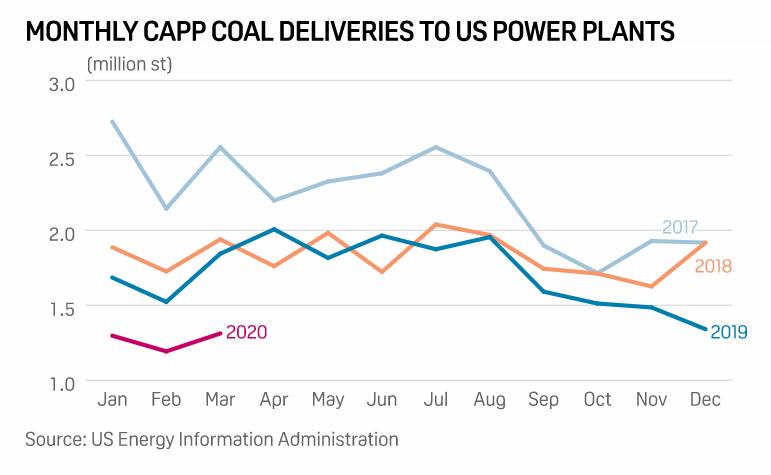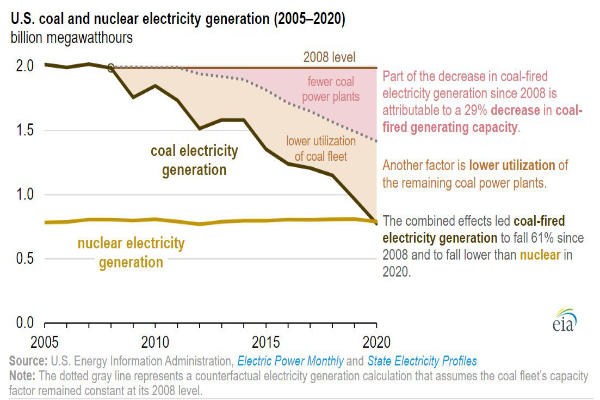
U.S. coal-fired electricity generated totaled 774 million megawatt hours (MWh) in 2020, which is less than both natural gas-fired (1.6 billion MWh) and nuclear-powered generation (790 million MWh), according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s (EIA) Electric Power Monthly.
Last year marked the first time that coal was not the largest or second-largest source of annual electricity generation in the United States since at least 1949. However, EIA expects U.S. coal-fired electricity generation to increase and for nuclear-powered electricity generation to decrease in both 2021 and 2022.
Coal-fired electricity generation in the United States has continued to decrease as coal-fired generating units have been retired or converted to use other fuels and as the remaining coal-fired generating units have been used less often. U.S. operating coal-fired electricity generation capacity measured 313 gigawatts (GW) in 2008. In that year, the earliest for which EIA’s State Electricity Profiles have capacity factor data, coal’s capacity factor was 72%.
Capacity factors measure the actual generation output for a fleet of generators as a percentage of what those generators are capable of generating. By 2020, coal’s operating capacity had fallen to 223 GW, and the coal fleet’s capacity factor had fallen to 40%.
Nuclear-powered generation was relatively steady in the previous decade. Although several nuclear power plants were retired, that decline in capacity was partially offset by upgrades at several plants and the addition of Watts Bar Unit 2 in Tennessee. U.S. nuclear power, with 97 GW of capacity in 2020, has less than half as much operating capacity as coal, but nuclear power plants are operated more intensively. Nuclear’s capacity factor in 2020 was 93%.
Source: IEA