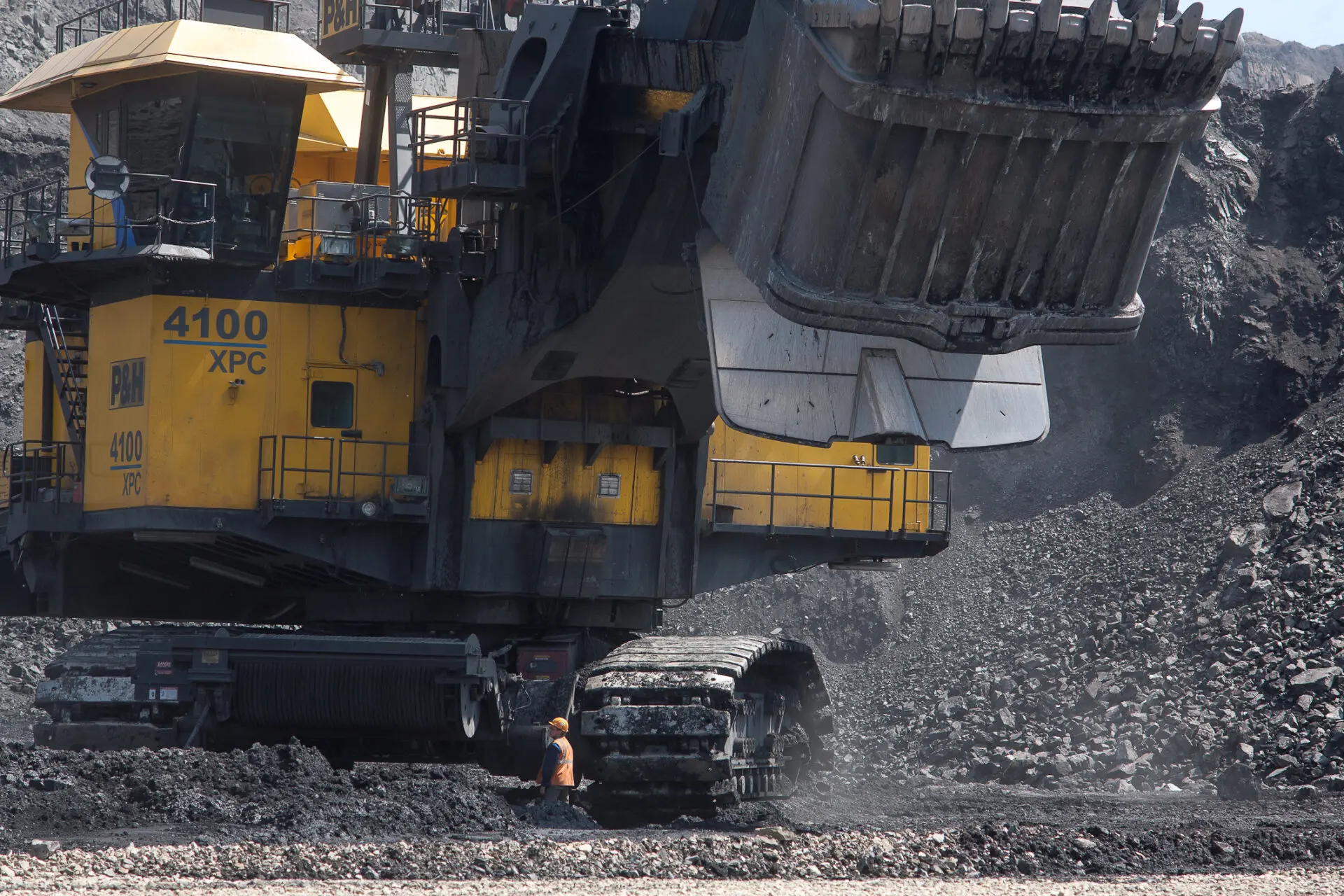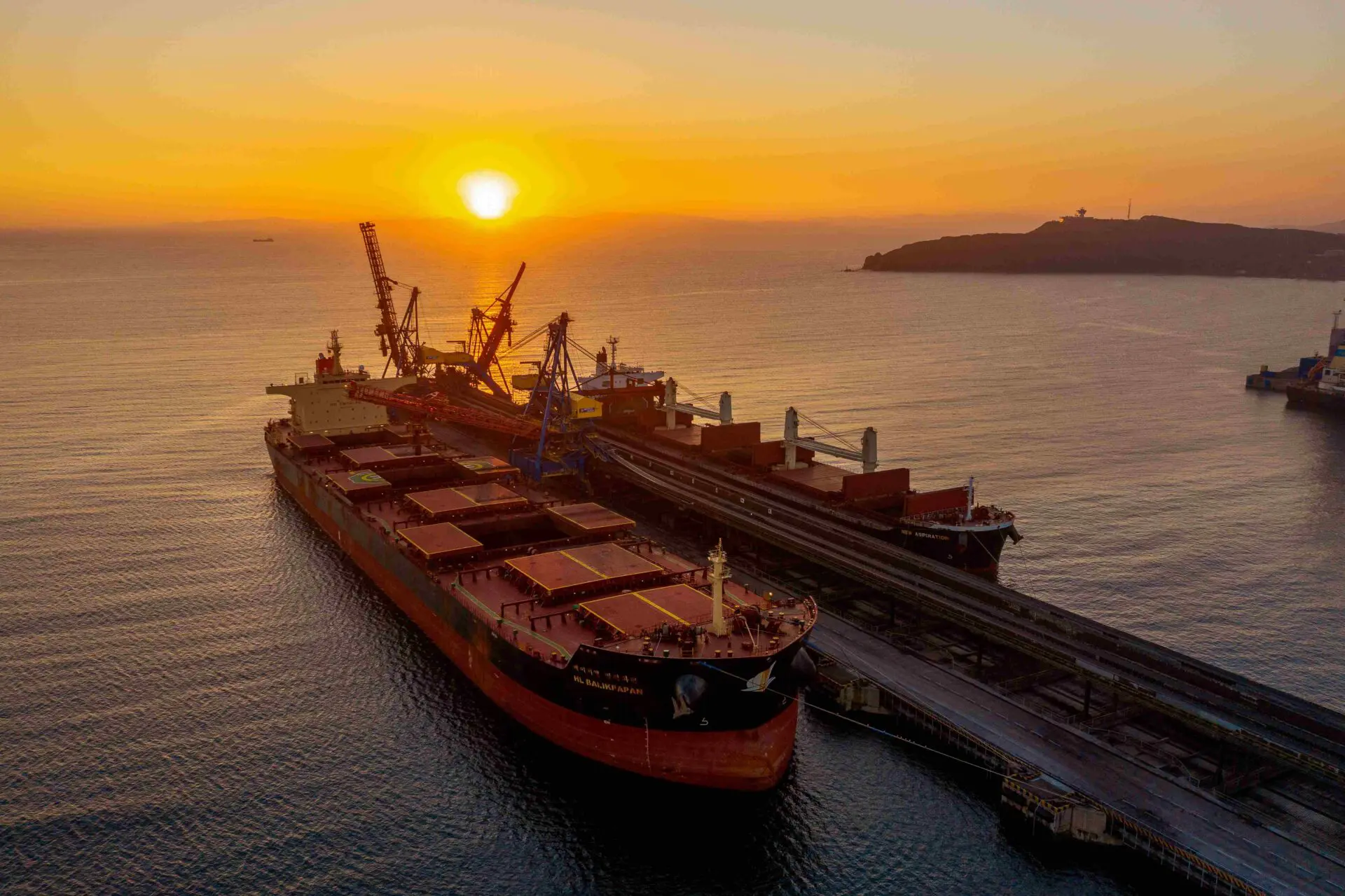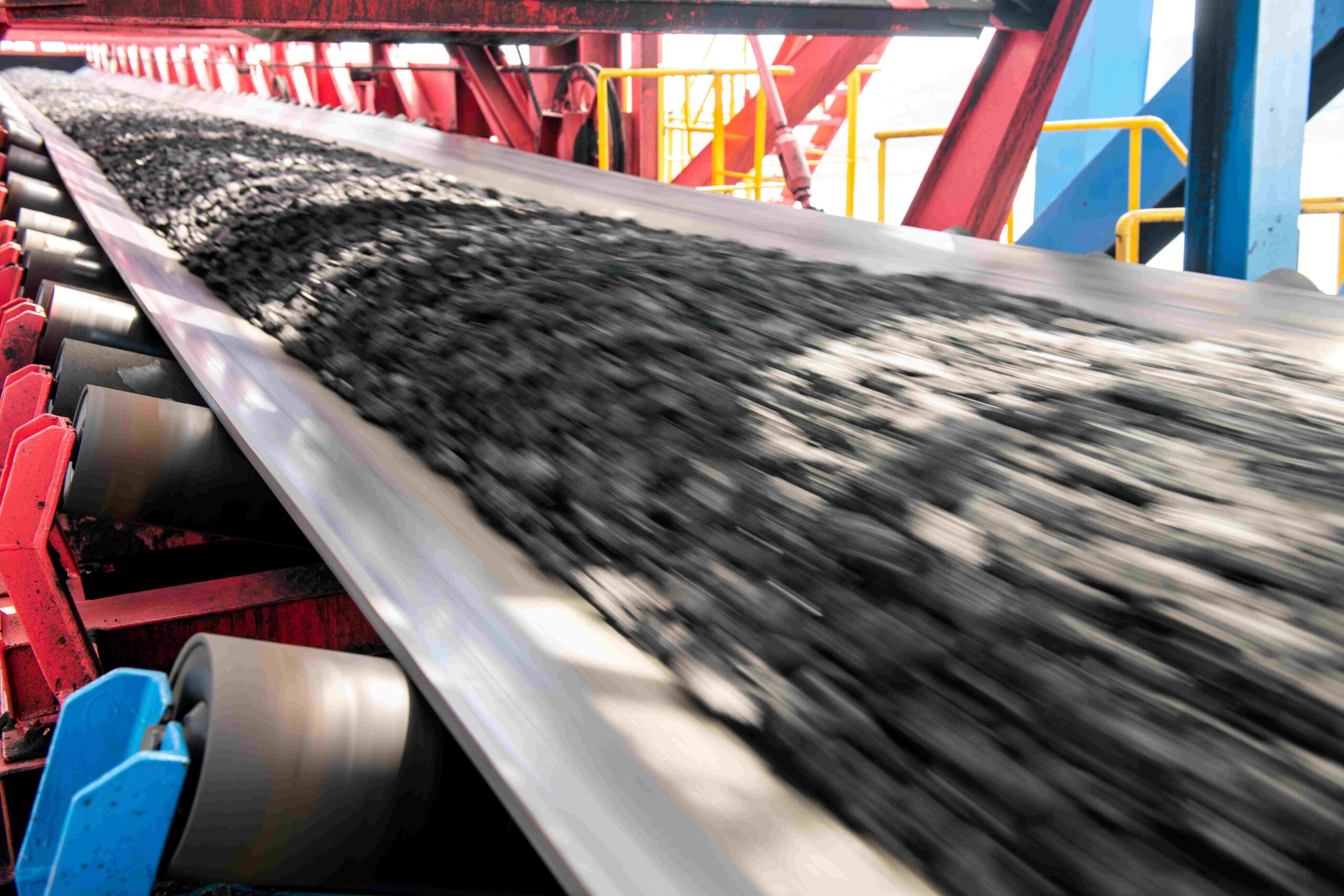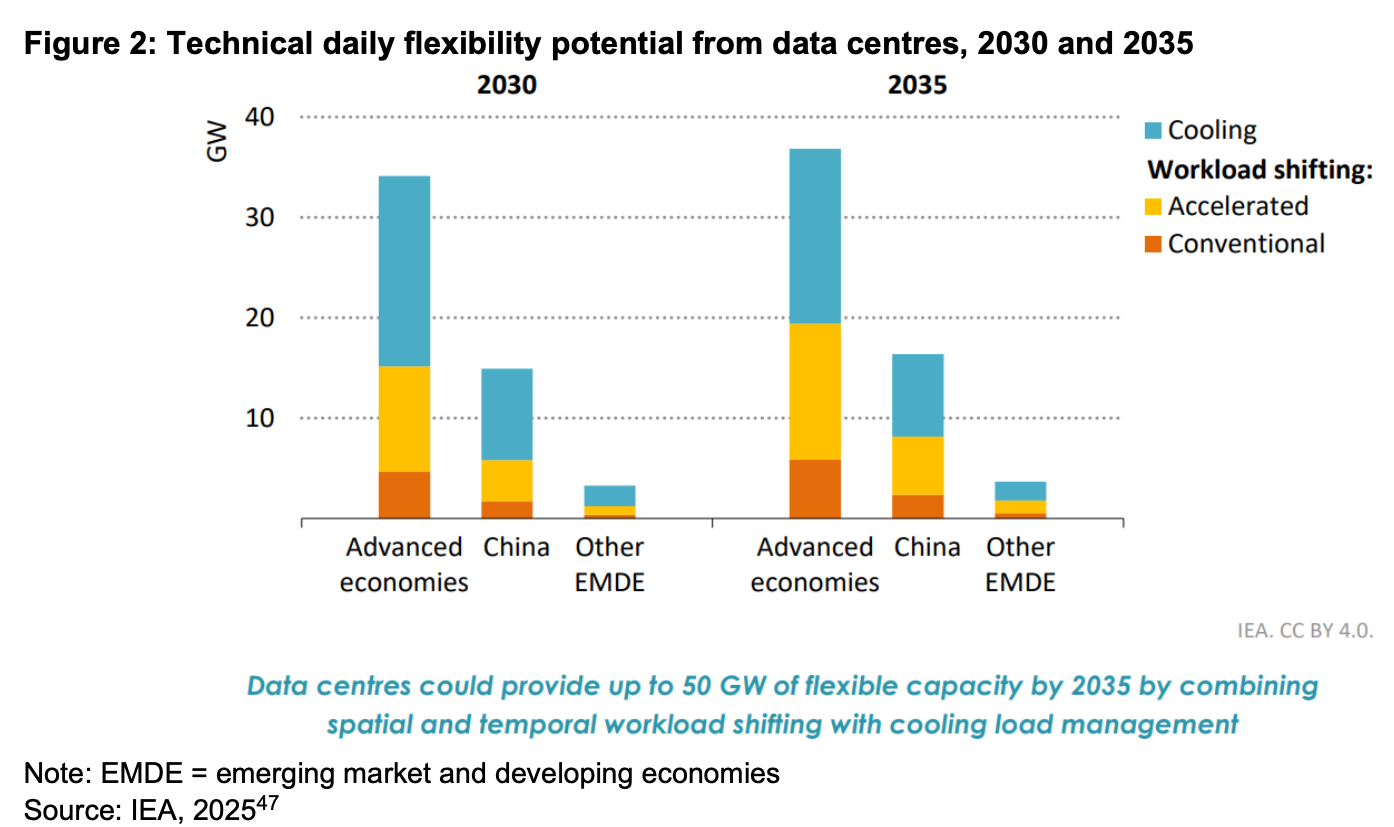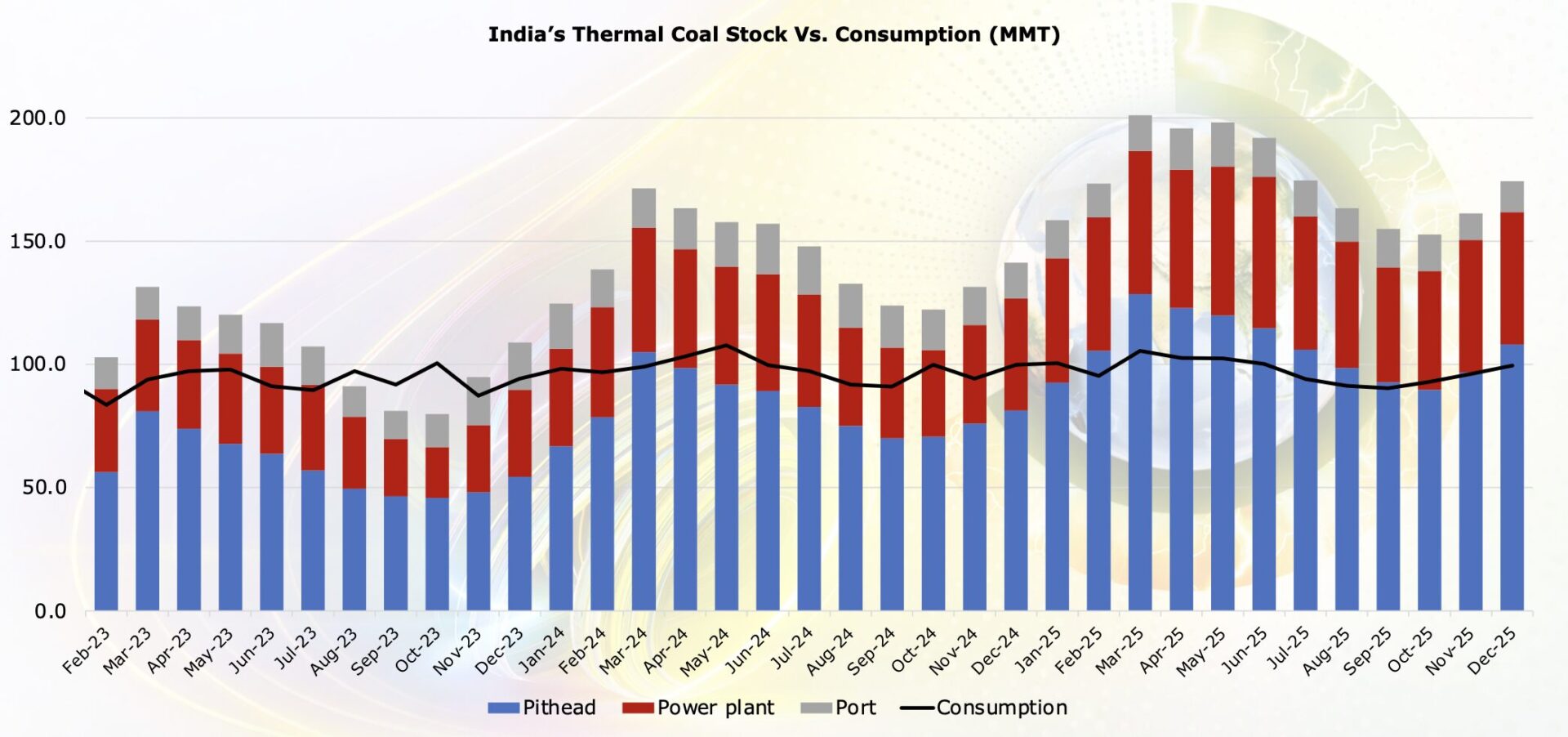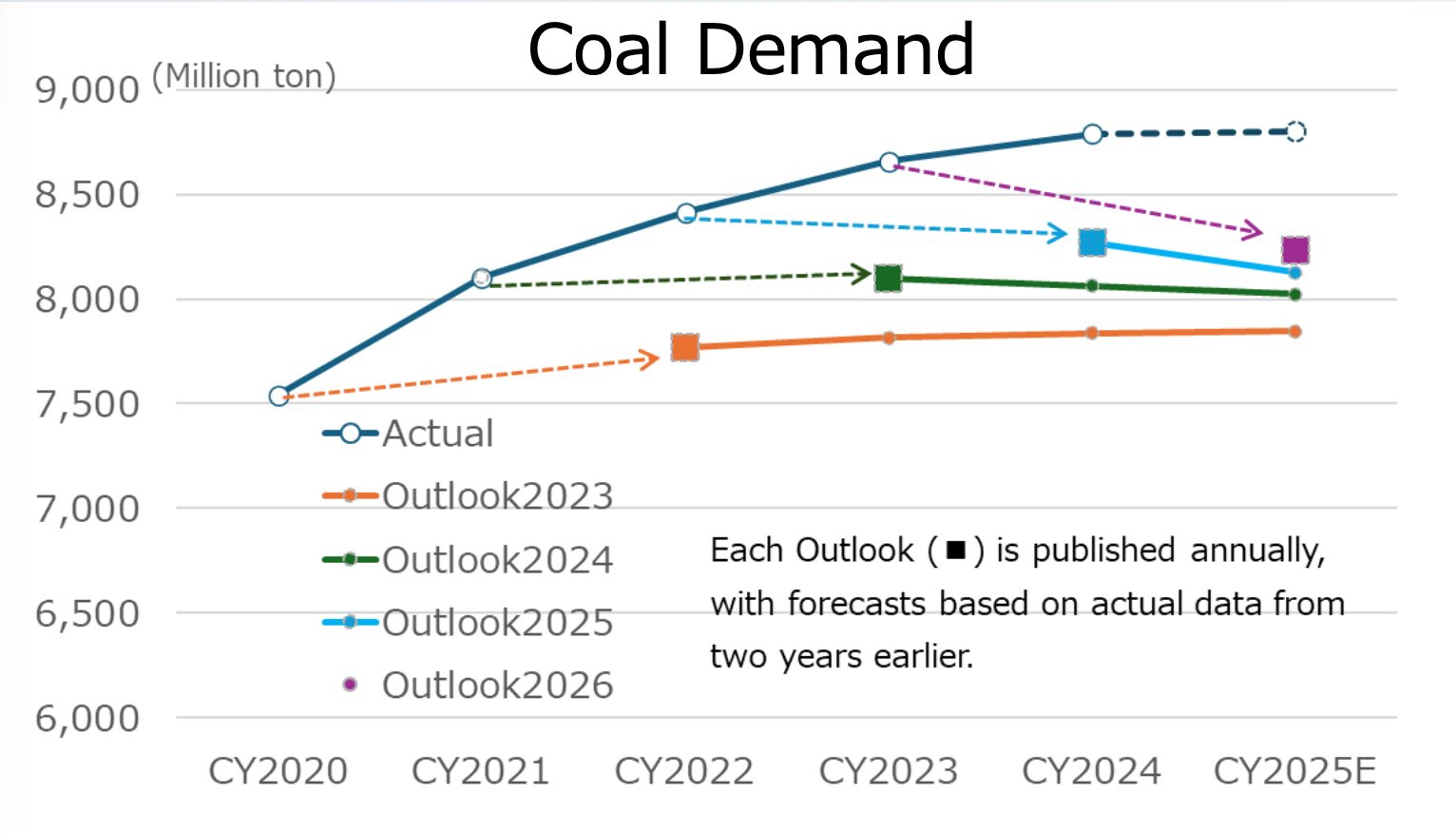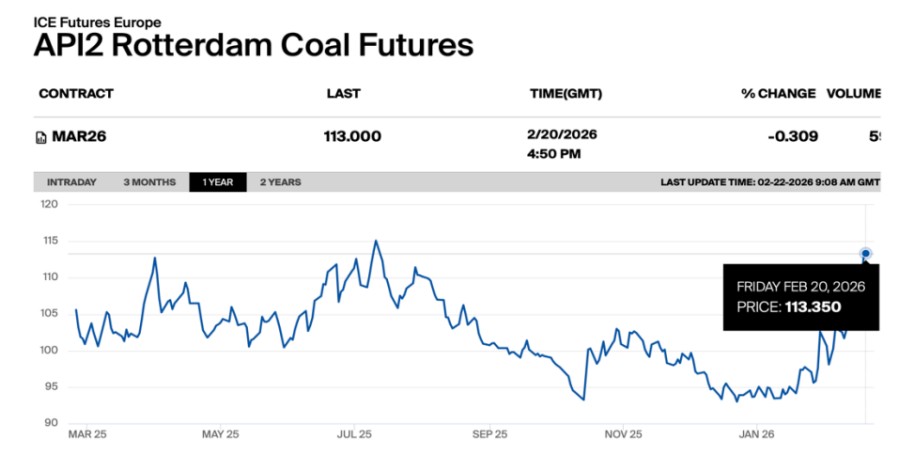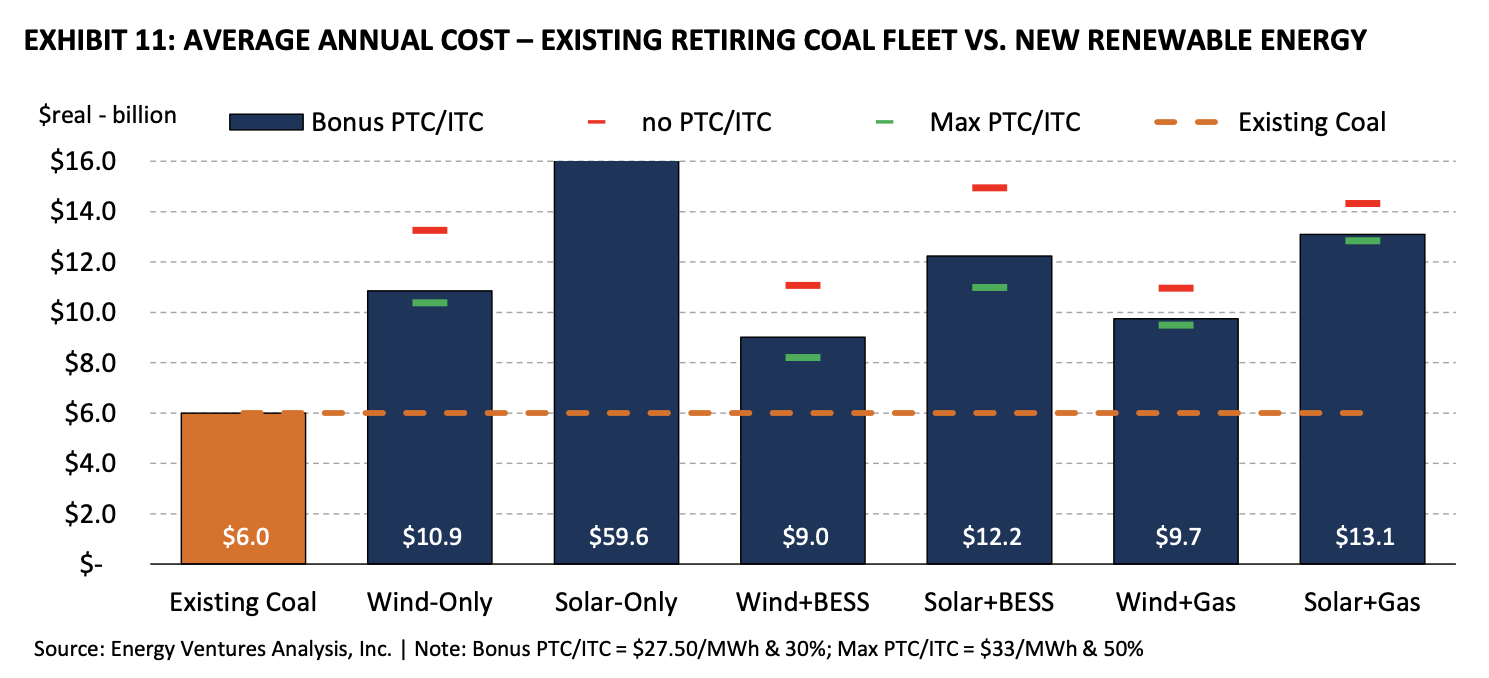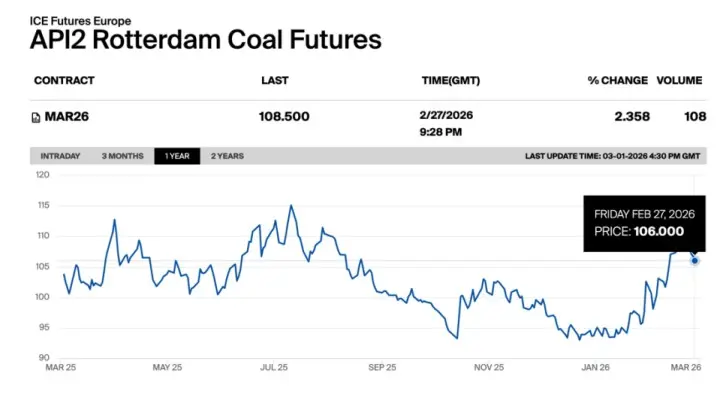

No single commodity is more important to America’s railroads than coal, which accounted for 38.8 percent of rail tonnage and 18.8 percent of rail revenue in 2014. Most coal in the United States is consumed at power plants. Historically, coal has dominated U.S. electricity generation because it is such a cost-effective fuel choice, and freight railroads are a big reason for that.
Approximately 70 percent of the coal delivered to coal-fueled power plants is delivered by rail. Electricity is also generated using other fuels, including nuclear power, wind, solar power, hydroelectric power, and natural gas. Recently, U.S. natural gas production has surged due to “fracking,” resulting in lower natural gas prices to electricity generators and increasing the competitiveness of electricity generated from natural gas vis-à-vis electricity generated from coal.
In addition, increasingly stringent environmental regulations have targeted coal-fueled generation. Consequently, electricity generated from coal — and associated rail coal volumes — have fallen. Whether this is a short- or a long-term phenomenon remains to be seen.